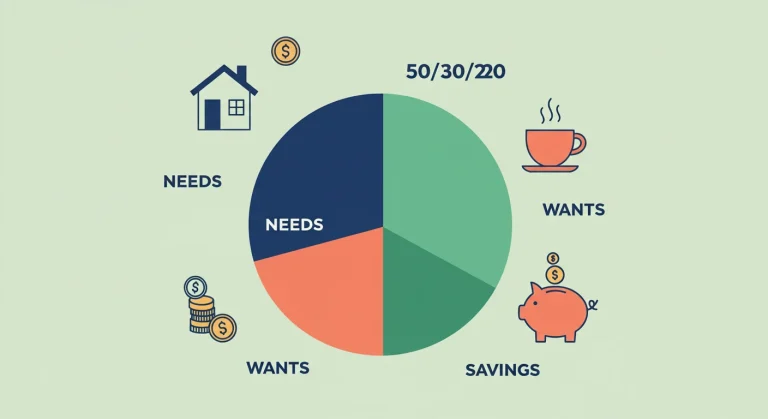
What does the 50 30 20 rule for budgeting represent? The 50 30 20 rule is a straightforward budgeting framework that emphasizes a balanced approach to managing personal finances. It categorizes your income into three essential segments: needs, wants, and savings. By allocating your income in this way, you can prioritize essential expenditures while ensuring that you also save and indulge in some non-essential spending. This rule is not only easy to understand but also effective for maintaining financial health and achieving long-term goals.
This budgeting rule has gained popularity in recent years due to its simplicity and effectiveness. With the rising cost of living and the increasing need for financial literacy, the 50 30 20 rule offers a practical solution for individuals looking to gain control over their finances. By clearly defining categories for different spending behaviors, users can make more informed financial decisions. This structured approach can especially benefit young professionals and those just beginning their financial journey.
Moreover, the 50 30 20 rule promotes discipline in spending, which can lead to significant long-term benefits, including reduced debt and enhanced savings. The clarity of this rule allows individuals to quickly assess their financial situation, making it a valuable tool for anyone struggling with budgeting. As more people seek to adopt better financial habits, understanding what the 50 30 20 rule for budgeting represents is critical for fostering a secure financial future.
In this article, we will explore the components of the 50 30 20 rule, delve into practical applications, discuss its advantages, and outline potential challenges. By the end of this discussion, you will have a comprehensive understanding of this budgeting technique and how to implement it effectively in your financial planning.
Understanding the 50 30 20 Rule
The 50 30 20 rule divides your after-tax income into three categories: needs, wants, and savings. Each category represents a percentage of your total income:
- 50% for Needs: This includes essential expenses such as housing, utilities, groceries, transportation, and insurance.
- 30% for Wants: Non-essential expenditures that improve your quality of life, including dining out, entertainment, hobbies, and vacations.
- 20% for Savings: Amount set aside for future goals, such as retirement, emergency funds, or debt repayment.
Practical Application of the 50 30 20 Rule
Implementing the 50 30 20 rule requires an assessment of your monthly income and expenses. Start by calculating your net income after taxes. Then, track your spending over a monthly period to identify how much is allocated to each of the three categories.
Once you’ve categorized your expenses, adjust your spending habits accordingly. This may involve cutting back on discretionary expenses or finding ways to save on fixed costs. Utilizing budgeting apps can greatly enhance the tracking process and help you stay within your limits.
Advantages of the 50 30 20 Rule
The advantages of this budgeting approach are numerous. Firstly, it promotes financial discipline by offering a clear breakdown of spending, ensuring that essential needs are met while still allowing for personal enjoyment.
Additionally, the 50 30 20 rule is flexible, accommodating various income levels and lifestyle choices. Whether you are a student, a young professional, or a retiree, this budgeting method is adjustable to fit your unique situation. Furthermore, it encourages the habit of saving, ultimately facilitating wealth-building for future prosperity.
Challenges of the 50 30 20 Rule
While the 50 30 20 rule presents an effective budgeting strategy, some challenges may arise. For instance, some individuals may find it difficult to categorize expenses accurately or to adhere strictly to the set percentages.
High cost of living in certain areas can also make it challenging to adhere to the 50% allocated for needs. Additionally, unexpected expenses can disrupt planned budgets, highlighting the need for flexibility and adaptation within this framework.
Making the Most of the 50 30 20 Rule
To maximize the effectiveness of the 50 30 20 rule, consider regularly reviewing and adjusting your budget. Set specific financial goals, whether they are short-term, like saving for a vacation, or long-term, such as retirement planning.
Incorporating regular financial check-ins with a trusted advisor can provide additional support and accountability, helping you stay on track. Finally, always be open to modifying your approach as your financial situation evolves, ensuring that your budgeting method remains convenient and effective.

Useful links
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 50 30 20 rule for budgeting is a straightforward and intuitive framework that can help individuals gain control over their finances. By allocating 50% of income to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt repayment, this model promotes a balanced approach to financial management. This method encourages individuals to prioritize their essential expenses while still permitting enjoyment through discretionary spending, all while ensuring a portion of their income is allocated to long-term financial security.
Moreover, the 50 30 20 rule is adaptable to various income levels and financial situations, making it a versatile tool for anyone seeking financial stability. It simplifies budgeting by breaking down complex financial decisions into manageable portions, making it easier for individuals to track their spending and adjust their habits accordingly. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for those new to budgeting or those who find traditional methods overwhelming.
Ultimately, adopting the 50 30 20 rule can lead to improved financial health and peace of mind. By understanding and implementing this budgeting guideline, individuals can create a sustainable financial plan that nurtures both their immediate needs and future aspirations. Whether you’re looking to pay down debt, save for a major purchase, or simply gain a better grasp of your finances, the 50 30 20 rule offers a proven strategy to achieve your goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the 50 30 20 rule for budgeting?
The 50 30 20 rule aims to simplify personal finance management by providing clear spending categories. It helps individuals allocate their after-tax income into three main categories: 50% for needs such as housing and food, 30% for wants like entertainment, and 20% for savings and debt repayment. This structured approach allows for easy tracking of expenses and promotes financial discipline, ultimately leading to better financial health.
Can I adjust the percentages in the 50 30 20 rule?
Yes, the percentages in the 50 30 20 rule can be adjusted based on your financial circumstances and goals. For instance, if you have high debt, you might allocate more than 20% to savings and debt repayment. Alternatively, if your income is low and your needs consume more than 50%, you may need to reassess your wants category. Flexibility is key, as the rule serves as a guideline rather than a strict formula.
How can I effectively track my spending using the 50 30 20 rule?
To track your spending effectively, start by categorizing your expenses according to the 50 30 20 framework. You can use budgeting apps, spreadsheets, or even pen and paper to log your expenses monthly. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your budgets based on actual spending will help you stay on target. Consider setting up alerts for when you approach the limits of each category, enabling real-time budget management.
What are some examples of needs under the 50 30 20 rule?
Needs refer to essential expenses necessary for basic living, such as housing costs (rent or mortgage), utilities, groceries, health insurance, transportation (like public transport or fuel), and minimum debt payments. Identifying these needs accurately is crucial, as they form the foundation of your financial obligations under the 50% allocation of your income.
How can I balance my wants without overspending?
Balancing your wants within the 30% allocation requires setting clear priorities. Determine what you value most in your discretionary spending—be it dining out, travel, or hobbies—and allocate accordingly. Establishing a budget for each category of wants, participating in impulse control practices, and regularly reviewing your expenditures can significantly help you stay within your limits while still enjoying life.
Is the 50 30 20 rule suitable for everyone?
While the 50 30 20 rule is a versatile and helpful framework, its suitability depends on individual financial situations. Those with unique incomes, high living costs, or distinct financial goals might require modifications. It’s advisable to adapt the rule to fit personal circumstances, ensuring it meets your specific needs and helps you achieve your financial objectives effectively.
What is the benefit of saving 20% of my income?
Saving 20% of your income provides various benefits, including building an emergency fund, paying off debt, and preparing for future investments or purchases. Regular savings foster financial stability, allowing you to handle unexpected expenses without resorting to credit. Furthermore, this disciplined approach can lead to substantial wealth accumulation over time, enhancing your security and ability to seize opportunities as they arise.